Creating a Service under Windows NT/2000/XP isn't hard. It requires a little knowledge of how services interact with the system, but once you've got a basic framework, a service works just like any other program. The advantages a service offers over a regular program is that it will automatically start up when Windows starts up, if it crashes, you can configure Windows to automatically restart it, and you can set it to run under any account you like (for example, to restrict how a hacker can damage your system), you can also start/stop services remotely.
Remember, though, that there are also a few drawbacks to services. The first is that only NT Windows'es can use services. This means you can't run your server on a Windows 98 machine for example (though why you'd want to, I don't know). Also, services usually cannot interact with the desktop. That is, except under certain circumstances, you can't use the [font="Courier New"]MessageBox[/font] function, or create windows, or anything like that.
I'll leave up it reader discretion as to whether a service best suits your needs, so let's just press ahead...
[size="5"]Setting Up
The first thing you need to do is create a project for your service. You can do this with any IDE you like (or you can even use make files if that's what floats your boat), but I like Visual C++. Most of the time you'll want to make a console project but a regular windows one works as well.
The very first thing you need to be able to do is install and uninstall your service from the control panel's service control manager. To see the service control manager, open the Control Panel, double-click on Administrative Tools, then on Services. I like to be able to install and uninstall my services from the command-line, with syntax like the following:
[font="Courier New"] C:\> MyService.exe -install[/font]
or:
[font="Courier New"] C:\> MyService.exe -uninstall[/font]
The first thing you need to do when accessing the service control manager (SCM) is open a handle to it. This is done with the [font="Courier New"]OpenSCManager()[/font] function, like this:
SC_HANDLE handle = ::OpenSCManager( NULL, NULL, SC_MANAGER_ALL_ACCESS );SC_HANDLE service = ::CreateService(
handle,
"MyService",
"MyService",
GENERIC_READ | GENERIC_EXECUTE,
SERVICE_WIN32_OWN_PROCESS,
SERVICE_AUTO_START,
SERVICE_ERROR_IGNORE,
"C:\\Path\\To\\Executable.exe",
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
NULL
);To uninstall the service, use code like this:
// first, open a handle to the service
SC_HANDLE service = ::OpenService( handle, "MyService", DELETE );
if( service != NULL )
{
// remove the service!
::DeleteService( service );
}Once you have the service installed, you'll be able to see something like this in the SCM applet:
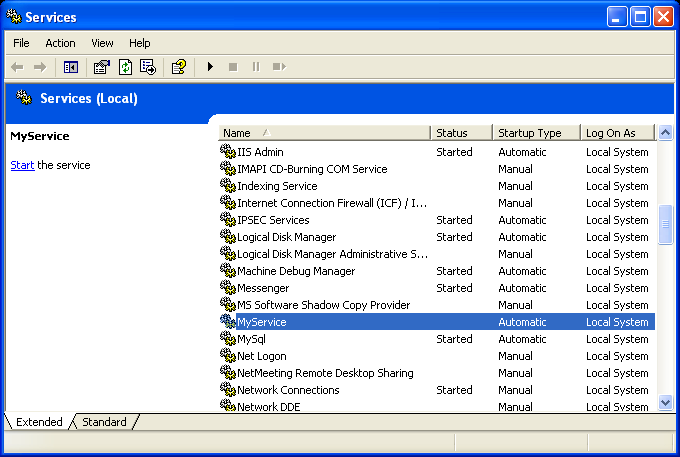
[size="5"]Running the Service
Once the service has been installed, you'll then be able to start and stop it from the service control manager applet. To this, you've got to add quite a bit of functionality to your framework. The first thing you need to do is start the Service Control Dispatcher. This is responsible for responding to requests from the SCM about starting, stopping or pausing the service.
The Service Control Dispatcher can handle requests for multiple services (for example, you can have multiple copies of your program running on the same machine, each with a different name). To facilitate this, you need to setup a Dispatch Table, which maps service names to dispatch handlers.
SERVICE_TABLE_ENTRY dispatchTable[] =
{
{ "MyService", &ServiceDispatch },
{ NULL, NULL }
};
if( ::StartServiceCtrlDispatcher( dispatchTable ) == 0 )
{
// if this fails, it's probably because someone started us from
// the command line. Print a message telling them the "usage"
}SERVICE_STATUS_HANDLE hStatus;
SERVICE_STATUS status;
void WINAPI ServiceDispatch( DWORD numArgs, char **args )
{
// we have to initialize the service-specific stuff
memset( &status, 0, sizeof(SERVICE_STATUS) );
status.dwServiceType = SERVICE_WIN32;
status.dwCurrentState = SERVICE_START_PENDING;
status.dwControlsAccepted = SERVICE_ACCEPT_STOP;
hStatus = ::RegisterServiceCtrlHandler( "MyService", &ServiceCtrlHandler );
// more initialization stuff here
::SetServiceStatus( hStatus, &status );
}The [font="Courier New"]ServiceCtrlHandler[/font] is another function that we write which actually responds to these service control requests. A basic version might look like this:
void WINAPI ServiceCtrlHandler( DWORD control )
{
switch( control )
{
case SERVICE_CONTROL_SHUTDOWN:
case SERVICE_CONTROL_STOP:
// do shutdown stuff here
status.dwCurrentState = SERVICE_STOPPED;
status.dwWin32ExitCode = 0;
status.dwCheckPoint = 0;
status.dwWaitHint = 0;
break;
case SERVICE_CONTROL_INTERROGATE:
// just set the current state to whatever it is...
break;
}
::SetServiceStatus( hStatus, &status );
}[size="5"] Debugging a Service
This is where things get tricky. You cannot debug a service that is not set to interact with the desktop, also, because of the way services work, you need to be able to attach your debugger to a running service.
To get over the first problem, you need to have the service run under the LocalSystem account and be able to "Interact with Desktop". To do this, right-click on your service, and go to Properties, go to the Log On tab, and check "Allow service to interact with desktop", as in the screen shot below:
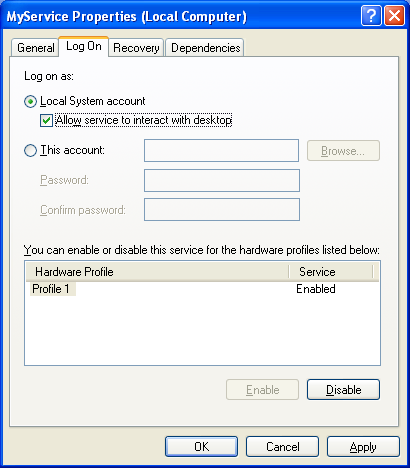
Next, to be able to actually debug the service, you've got to get your debugger to attach to the running process. This can be done two ways. When the service has started, you can right-click on the process name in the Task Manager and select Debug from the menu. This will start up your debugger and you can then set break-points and such to your heart's content.
Another method is to insert a call to [font="Courier New"]DebugBreak[/font] in you code somewhere. Then, when it get's there, it'll raise an exception and Windows will let you attach the debugger. You'll need to step out of the [font="Courier New"]DebugBreak[/font] function before you'll be able to see any source code, though...
[size="5"]End Game
And that's pretty much all you need to know! The example framework that I've included add quite a bit of functionality to what I've described here. For example, you can start and stop the service from the command-line, and you can run the service and a regular windows console application. This is good because it makes debugging easier.
If you have any comments or questions, don't hesitate to mail me: [email="dean@codeka.com"]dean@codeka.com[/email].
[hr]
Codeka.com - Just click it.



