Introduction: What Is A Decal?
So what exactly is a decal, you may ask? Well, the American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language describes a decal as:
- A picture or design transferred by decalcomania.
- A decorative sticker.
- The process of transferring pictures or designs printed on specially prepared paper to materials such as glass or metal.
- A decal.
In this article we will use the coordinate system found in 3D Studio Max, where, with respect to your computer monitor, +X is right, +Y is into the screen and +Z is up. So if you're looking down on the terrain (your line of sight is parallel with the Z-axis), the Y & X axis appear as they would in the Cartesian coordinate system. You can now forget about the Z-axis, as a terrain's Z-axis displacement, i.e. it's height, has no effect on our decals and is thus of no consequence. To make proceedings even simpler, we're going to place our terrain entirely in the first Cartesian quadrant, that is, the quadrant that is positive in both the x and y directions.
Cell Alignment and Texture Clamping
A cell is a square segment consisting of two triangle primitives belonging to a uniform terrain grid. As you would expect, decals do not always cover a complete cell or cells of a terrain, in fact, they are almost always found upon a fraction of a cell. To display a decal over a fraction of a cell we need to set the decal's texture to 'clamp to the edge', this tells the graphics card to map edge texels to adjacent polygon regions that have texture UVs below zero or above one.
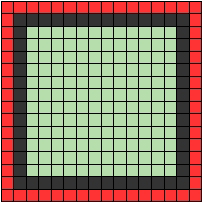
[Figure 1] The red pixels at the edge of the decal are set to full transparency.
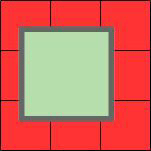
[Figure 2] The repeated edge pixels have no transparency, causing the decal to cover all nine cells.
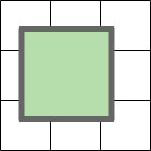
[Figure 3] The repeated edge pixels cannot be seen, displaying the decal over a fraction of the cells.
A problem may occur when a decal texture is resized to a smaller resolution. Transparent edge texels becoming compromised from blending with adjacent, non-transparent texels. The fix this problem the transparent border of the decal texture is widened, so that when resizing occurs, there will still be fully transparent texels at the edge of the texture.
Texture Coordinates
To utilize our texture clamp settings we now need to calculate the appropriate texture coordinates for our decal mesh. If our decal is not aligned to the top left corner of our mesh, then the decal texture offset will be greater than zero.
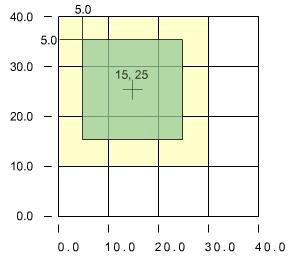
[Figure 4] The decal has a texture offset of x:5 by y:5
We use this offset, along with the decal's size, to calculate the mesh's texture coordinates. Here is the code to generate the array of texture coordinates. Note that the texture array is a bottom-left to top-right column incremented data structure i.e. it starts with the bottom left grid vertex and ends with the top-right vertex.
// These values have been derived from Figure 4 Vector2 decalOffset = { 5.0f, 5.0f }; Vector2 decalPosition = { 15.0f, 20.0f }; Vector2 meshPosition = { 15.0f, 20.0f }; float fDecalWidth = 20.0f; float fDecalHeight = 20.0f; float fMeshWidth = 30.0f; float fMeshHeight = 30.0f; float fHalfDecalWidth = fDecalWidth / 2.0f; float fHalfDecalHeight = fDecalHeight / 2.0f; float fHalfMeshWidth = fMeshWidth / 2.0f; float fHalfMeshHeight = fMeshHeight / 2.0f; float fCellWidth = 10.0f; float fCellHeight = 10.0f; int verticesX = 4; int verticesY = 4; // how far from the top-left corner of the mesh does the decal start decalOffset.x = ( decalPosition.x - fHalfDecalWidth ) - ( meshPosition.x - fHalfMeshWidth ); decalOffset.y = ( fMeshHeight - fDecalHeight ) - (( decalPosition.y - fHalfDecalHeight ) - ( meshPosition.y - fHalfMeshHeight )); float invDecal.x = 1.0f / decalWidth; float invDecal.y = 1.0f / decalHeight; int x; int y; int index; int t; for( x = 0; x < verticesX; x++ ) { index = verticesY - 1; for( y = 0; y < verticesY; y++ ) { // get the index into the texture array t = ( x * verticesY ) + y; // calculate the uv coordinates for the vertex at t vertex[t].u = ( ( x * fCellWidth ) * invDecal.x ) - ( decalOffset.x * invDecal.x ); vertex[t].v = ( ( index * fCellHeight ) * invDecal.y ) - ( decalOffset.y * invDecal.y ); --index; } } And the results:
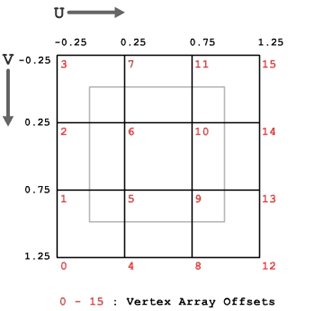
[Figure 5] The resulting texture coordinates
As we can see in Figure 5, there are UV values below zero and above one. Any part of the mesh that falls under those regions will be painted with a transparent texel.
Ripping Vertices and Pre-Calculating Indices
We want the decal to be the right shape so that is can match the slopes of the terrain perfectly. To accomplish this we must grab the existing vertices from the terrain. This process will vary depending on how you store your terrain data, as pulling vertices out of a tree hierarchy will evidently require a different technique to that of a simple vertex array. But once you have the vertices copied into the mesh, it only takes a translation or two to get them into decal space. As for indices, when using a uniform grid and creating many decals of the same size, it makes sense to pre-compute the indices and store them in a shared index buffer. Once the mesh is complete it's time to insert it into the scene graph. Make sure the mesh is raised slightly above the terrain to avoid z-buffer sorting issues.
Conclusion
Well that just about wraps up the essentials for terrain decals. Thanks to my AIE tutors (http://www.aie.act.edu.au/about/staff.php) for all of their help and guidance. I hope this article can assist anyone looking for a simple terrain decal solution, if you have any questions/abuse/job offers feel free to email me at [email="gtowse@yahoo.com"]gtowse@yahoo.com[/email]. Thanks for reading.




